|
Definition of Infrared Thermography |
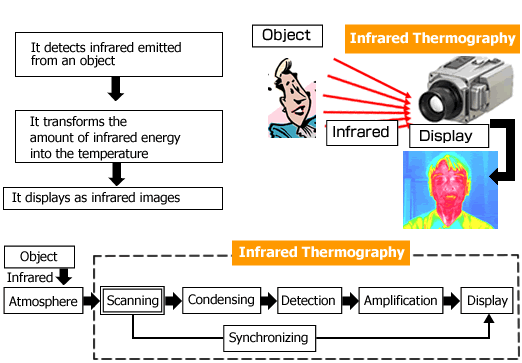
| Infrared thermography is equipment or method, which detects infrared energy emitted from object, converts it to temperature,
and displays image of temperature distribution. To be accurate, the equipment and the method should be called differently,
the equipment to be called as infrared thermograph and the method to be called as infrared thermography. Recently, however,
more and more public literatures show tendency not to pay attention to such appellative. We call our equipment as infrared
thermography considering such generalization of the terminology. |
|
|
| |
 |
Characteristics of Infrared Thermography equipment |
- It captures as a temperature distribution on a surface,and it can display as a visible information.
- Temperature can be measured from a distance without contacting an object.
- Temperature can be measured in real time.
|
| |
 |
Merits of Infrared Thermography equipment |
- Relative comparison of distribution of surface temperature can be made over a wide area.
- Temperature can be measured easily for a moving object or an object which is dangerous to get close to.
- Temperature of small object can be measured without confusing the temperature.
- Temperature of food, medicine or chemicals can be measured in a sanitary fashion.
- Temperature of an object with drastic temperature change or a phenomenon during a short period of time can be measured.
|
| |
|
Infrared Thermography equipment, Things often misunderstood |
| |
- <Q> Isn't infrared camera emitting something?
<A> No, it is not emitting anything: It merely detects infrared emitted from an object in a passive
manner. It should be noted, however, that it may be affected by the reflection from the vicinity.
- <Q> Isn't the temperature measured by the wave length You can see an object behind something
through it, can't you?
<A> No, Temperature distribution is measured by the amount of infrared energy.
- <Q> You can see an object behind something through it, can't you?
<A> No, Because infrared emitted from the surface of an object is detected, you cannot see through
something. However, you may be able to estimate the rear side if there is a temperature distribution appearing on the surface
due to the difference in heat conductivity.
|
| |
|
What is Infrared Thermography? |
| |
- Discovery of infrared
It was discovered by a British astronomer, Herschel, in 1800. When dispersing sunlight using a prism, Herschel accidentally
found that there was an invisible light on the outside of red light when increases the temperature of an object.
- It is an electromagnetic wave
Wavelength is 0.7µm or longer Wavelength is 1mm or less = Frequency is 300GHz or more.
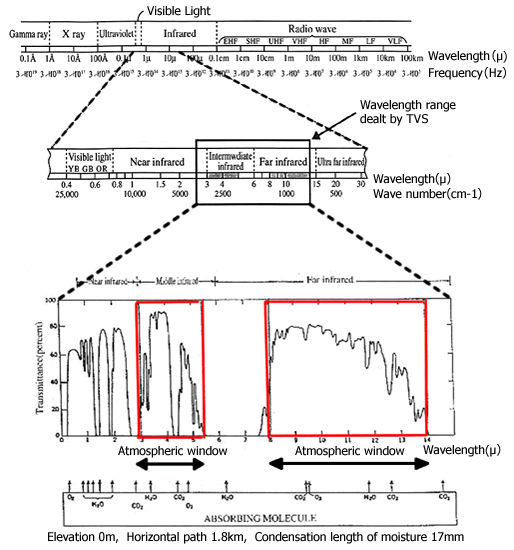
The source : R.D.Hudson, Jr. "INFRARED SYSTEM ENGINEERING" (John Wiley & Son, 1969)
|
|
Characteristics of infrared |
| |
- It is invisible since its wavelength is longer than visible light. It has nothing to do with brightness or darkness
of visible light
- It is emitted naturally from any object of which temperature is absolute zero(0K) or higher. Therefore, it can be applied
to any field
- It has a characteristic of heating an object. Therefore, it is sometimes called "heat wave".
- It is a kind of light (electromagnetic wave) It can be transmitted through vacuum.
- There is a correlation between infrared energy and temperature of an object. Therefore, it can be used to measure the
temperature of an object
|
| |
|
|
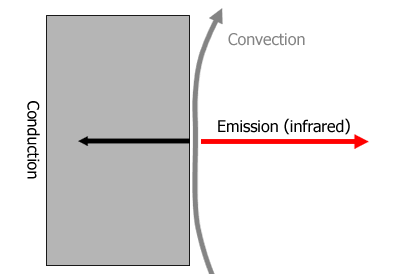
How the heat transfers |
| |
- Emission:
A type of heat transfer where the heat is transferred directly from the surface of an object as an infrared energy.
- Convection:
A type of heat transfer where the heat is transferred by the heated part of gas or liquid moving upward.
- Conduction:
A type of heat transfer mainly through a solid object
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
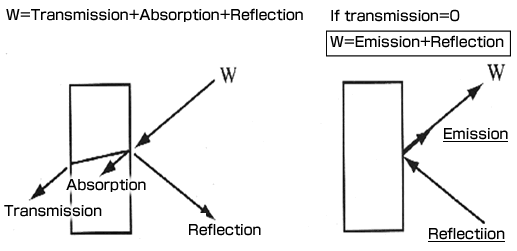
Emission, reflection and transmission of infrared |
| |
| An object which absorbs infrared well emits infrared well |
| |
 |
| |
|
 |
Principle of measurement by Infrared Thermography equipment |
|
| |
 |
Image Format of Infrared Thermography |
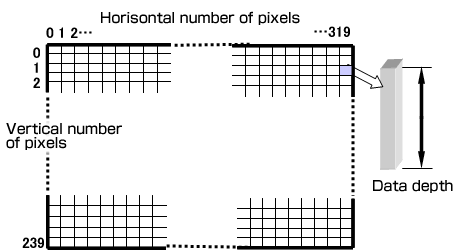
| Arrangement of detector and image data of infrared thermography |
|
| Temperature distribution image data |
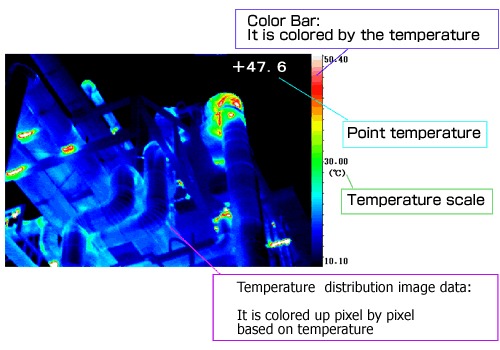 |
| Temperature distribution image data of infrared thermography consists of matrix of pixels (number of detector:
for example, 320 horizontal X 240 vertical pixels) as shown in the figure above. Thermal image data can be transferred to
PC. Subsequently, the data can be calculated and utilized freely. Thermal image data is colored up pixel by pixel based on
temperature. |
|